Csharp Structure
Dictionary
C# Dictionary class is a generic collection of keys and values pair of data.
Defined in the System.Collections.Generic namespace is a generic class and can store any data types in a form of keys and values. Each key must be unique in the collection.
1 | using System.Collections.Generic; |
1 Add elements to a C# Dictionary
1 | Dictionary<string,string> EmployeeList=new Dictionary<string,stirng>(); |
2 Retrieve elements from a C# Dictionary
1 | foreach(KeyValuePair<string,Int16> author in AuthorList) |
3 C# Dictionary Properties
Count, Keys and Values.
4 Get number of elements in a C# Dictionary
The Count property gets the number of key/value pairs in a Dictionary.
1 | Console.WriteLine("Count: {0}", AuthorList.Count); |
5 Get a Dictionary item
The Item property gets and sets the value associated with the specified key.
1 | // Set Item value |
6 Get the collection of keys of C# Dictionary
1 | // Get and display keys |
7 Get the collection of values of a C# Dictionary
1 | // Get and display values |
8 C# Dictionary Methods
The Dictionary class is a generic collection and provides all common methods to add, remove, find and replace items in the collection.
9 Add Items
1 | Dictionary<string, Int16> AuthorList = new Dictionary<string, Int16>(); |
10 Remove elements from a C# dictionary
1 | // Remove item with key = 'Mahesh Chand' |
11 Find a key in a Dictionary
The ContainsKey method checks if a key is already exists in the dictionary.
1 | if (!AuthorList.ContainsKey("Mahesh Chand")) |
12 Find a Value in a Dictionary
The ContainsValue method checks if a value is already exists in the dictionary.
1 | if (!AuthorList.ContainsValue(9)) |
Queue
Queue represents a first-in, first-out (FIFO) collection of objects.
1 Queue Constructors
1 | //Queue<T> Constructor |
2 Queue.Count Property
The Count property gets the number of elements of Queue<T>.
1 | namespace Queue { |
3 Queue.Enqueue()
The Queue.Enqueue method adds an object to the end of the Queue
1 | namespace Queue { |
4 Queue.Dequeue()
Removes and returns the object at the beginning of the Queue
1 | namespace Queue { |
5 Queue.contain()
Determines whether an element is in the Queue
1 | namespace Queue { |
6 Queue.Clear()
Removes all objects from the Queue
7 Queue.Peek()
Returns the object at the beginning of the Queue
8 Queue.ToArray()
Copies the Queue
1 | namespace Queue { |
Stack
A stack is a LIFO (last in first out) data structure.
1 Stack Constructors
Stack
Stack
Stack
2 Stack.Count Property
he Count property of the Stack class returns the number of elements in a stack.
3 Stack.Push()
The Push() method is used to add a (push) element to the stack.
4 Stack.Pop()
The Pop() method is used to remove elements from a stack. The Pop() method removes the top most item from the stack.
5 Stack.Peek()
The Peek() method returns the topmost element of a Stack
6 Stack.Clear()
The Clear() method of Stack
List
The C# List
1 | using System.Collections.Generic; |
1 List Constructors
1 | // List with default capacity |
2 List.Add()
The Add method adds an element to a List.
3 List Properties
- Capacity – Number of elements List
can contain. The default capacity of a List is 0. - Count – Number of elements in List
.
4 List.Insert()
The Insert method of List class inserts an object at a given position. The first parameter of the method is the 0th based index in the List.
The InsertRange method can insert a collection at the given position.
1 | authors.Insert(3, "Bill Author"); |
5 List.Remove()
1 | //he Remove method removes the first occurrence of the given item in the List. |
6 List.IndexOf()
The IndexOf method finds an item in a List. The IndexOf method returns -1 if there are no items found in the List.
1 | int idx = authors.IndexOf("Naveen Sharma"); |
7 List.Sort()
The Sort method of List
8 List.Reverse()
The Reverse method of List
9 List.BinarySearch()
The BinarySearch method of List
1 | int bs = authors.BinarySearch("Mahesh Chand"); |
HashTable
The Hashtable in C# is a collection that stores (Keys, Values) pairs.
The Keys are used to find the storage location.
The Base Class libraries offers a Hashtable Class that is defined in the System.Collections namespace.
1 HashTable Constructors
1 | Hashtable HT = new Hashtable(); |
2 Properties of Hashtable
- Comparer: Gets or Sets the IComparer to use for the Hash Table.
- Count: Gets the number of key/value pairs contained in the hash table.
- IsReadOnly: Get a value indicating whether the hash table is read-only.
- Item: Gets or Sets the value associated with the specified Key.
- Keys: Gets an ICollection containing the keys in the hash table.
- Values: Gets an ICollection containing the values in the hash table.
3 Methods of HashTable
- Add: Adds an element with the specified key and value in the hash table.
- Clear: Removes all the elements in the hash table.
- ContainsKey: Determined whether the hash table contains a specified key or not.
- ContainsValue: Determined whether the hash table contains a specified value or not.
StringCollection
StringCollection class is a new addition to the .NET Framework class library that represents a collection of strings.
StringCollection class defined in the System.Collections.Specialized namespace represents a collection of strings and provides functionality to manage the collection.
1 StringCollection Constructor
1 | using System.Collections.Specialized |
2 Adding Strings
- Add
- AddRange
- Insert
Add method is used to add string to a StringCollection at the end of the collection.
1 | // Add string using Add method |
AddRange method is used to add an array of strings to a StringCollection at the end of the collection.
1 | // Add an array of string using AddRange |
Insert method is used to insert a string at the specified location of a StringCollection.
1 | // Insert an string at a specified index |
3 Accessing Strings
The foreach loop statement in C# is used to iterate through a collection of objects such as integer or string.
1 | StringCollection authorNames = new StringCollection(); |
4 Removing Strings
- Clear
- Remove
- RemoveAt
Clear method removes all items from a StringCollection.
1 | authorNames.Clear(); |
Remove method removes the first occurrence of a given string from the string collection.
1 | authorNames.Remove("Mike Gold"); |
RemoveAt method removes a string specified at the given location from the string collection.
1 | authorNames.RemoveAt(5); |
5 Find String
IndexOf method searches for the specified string and returns the zero-based index of the first occurrence within the StringCollection.
1 | int authorLocation = authorNames.IndexOf("Mike Gold"); |
Contains method returns true if a string is found in a StringCollection.
1 | if (authorNames.Contains("Mike Gold")) |
6 Copy Strings
CopyTo method of StringCollection is used to copy items from a StringCollection to an array.
1 | // Copy Collection to new Array |
7 Count Strings
Count property returns total number of items in in a StringCollection.
8 Getting Items
ArrayCollection is a collection. That means, you can access its items by using an index.
HashSet
C# HashSet is an unordered collection of the unique elements.
System.Collections.Generic
1 HashSet Constructor
1 | HashSet < string > names = new HashSet < string > { |
2 HashSet.Add()
1 | names.Add("Rajeev"); |
3 HashSet.UnionWith()
1 | HashSet < string > names = new HashSet < string > { |
4 HashSet.IntersectWith()
This method combines the elements that are common to both the collections.
1 | names.IntersectWith(names1); |
5 HashSet.ExceptWith()
This method removes all the elements that are present in the other collections from the collection on which it is called.
LinkedList
Linked List is a linear data structure which consists of a group of nodes in a sequence. Each node contains two parts.
- Data− Each node of a linked list can store a data.
- Address − Each node of a linked list contains an address to the next node, called “Next”.
1 Types of Linked List
Singly Linked List: Singly linked lists contain nodes which have a data part and an address part, i.e., Next, which points to the next node in the sequence of nodes. The next pointer of the last node will point to null.
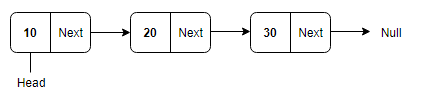
Doubly Linked List: In a doubly linked list, each node contains two links - the first link points to the previous node and the next link points to the next node in the sequence.The prev pointer of the first node and next pointer of the last node will point to null.
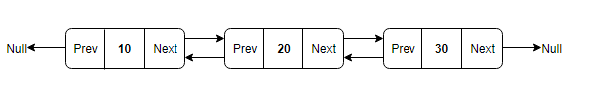
Circular Linked List: In the circular linked list, the next of the last node will point to the first node, thus forming a circular chain.
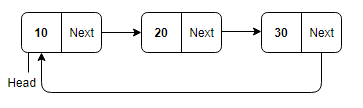
Doubly Circular Linked List: In this type of linked list, the next of the last node will point to the first node and the previous pointer of the first node will point to the last node.

2 Creating a Linked List
1 | //Singly linked list |
